In April, there were 43 volunteers in a cleanup project. Each volunteer was asked to choose a small gift labeled...
GMAT Problem-Solving and Data Analysis : (PS_DA) Questions
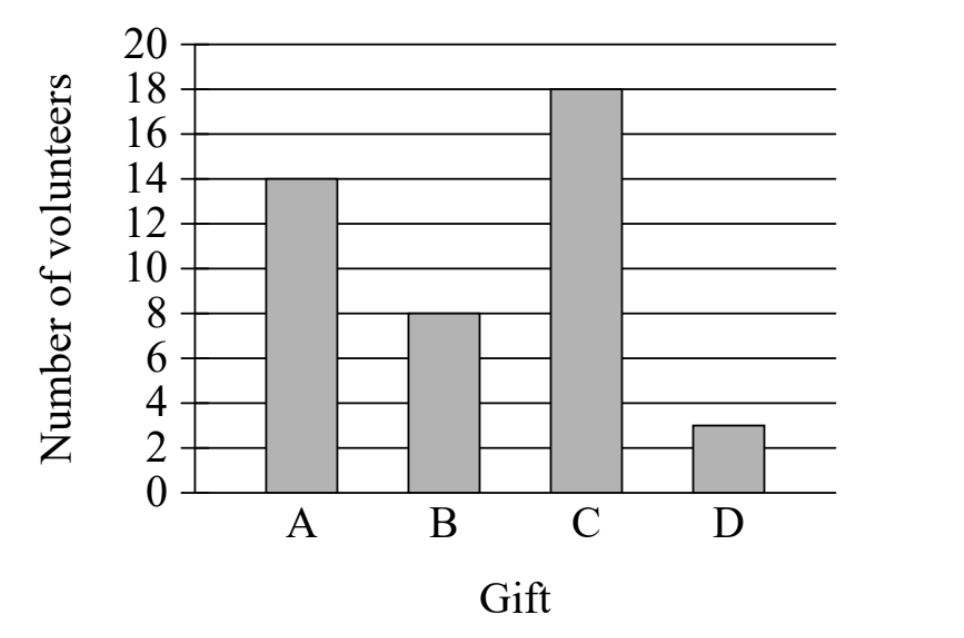
In April, there were 43 volunteers in a cleanup project. Each volunteer was asked to choose a small gift labeled A, B, C, or D. The bar graph shows the number of volunteers who chose each gift. How many volunteers chose gift C?
[Bar graph showing Number of volunteers (y-axis, 0-20) vs Gift (x-axis, A, B, C, D). The bars show: A = 14, B = 8, C = 18, D = 3]
1. TRANSLATE what the question is asking
The question asks: "How many volunteers chose gift C?"
- We need to find the number of volunteers represented by bar C in the graph
2. TRANSLATE the bar graph to get the answer
- Look at the x-axis (horizontal) to locate the bar labeled "C"
- The bars are arranged in order: A, B, C, D from left to right
- Once you've identified bar C, look at its height
- Follow the top of bar C horizontally to the y-axis
- Read the value on the y-axis where the top of bar C aligns
- The top of bar C reaches the line marked 18
- Therefore, 18 volunteers chose gift C
Answer: 18 (Choice D)
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak TRANSLATE skill - Reading the wrong bar:
Students who rush through the problem may look at the graph but accidentally read the height of a different bar instead of bar C. This happens when they don't carefully match the x-axis label to the correct bar.
- Reading bar A (height 14) leads them to select Choice C (14)
- Reading bar B (height 8) leads them to select Choice B (8)
- Reading bar D (height 3) leads them to select Choice A (3)
Notice that each wrong answer choice corresponds exactly to the height of a different bar - this is intentional test design to catch careless errors.
The Bottom Line:
This problem tests fundamental graph literacy - the ability to accurately read information from a visual display. While conceptually simple, it requires careful attention to match the correct label (gift C) with its corresponding bar and accurately read the y-axis value. All three incorrect answer choices are trap answers corresponding to the other three bars, so precision in identifying bar C is essential.