The absolute value function f is defined by an equation in the form \(\mathrm{f(x) = a|x + b| + c}\),...
GMAT Advanced Math : (Adv_Math) Questions
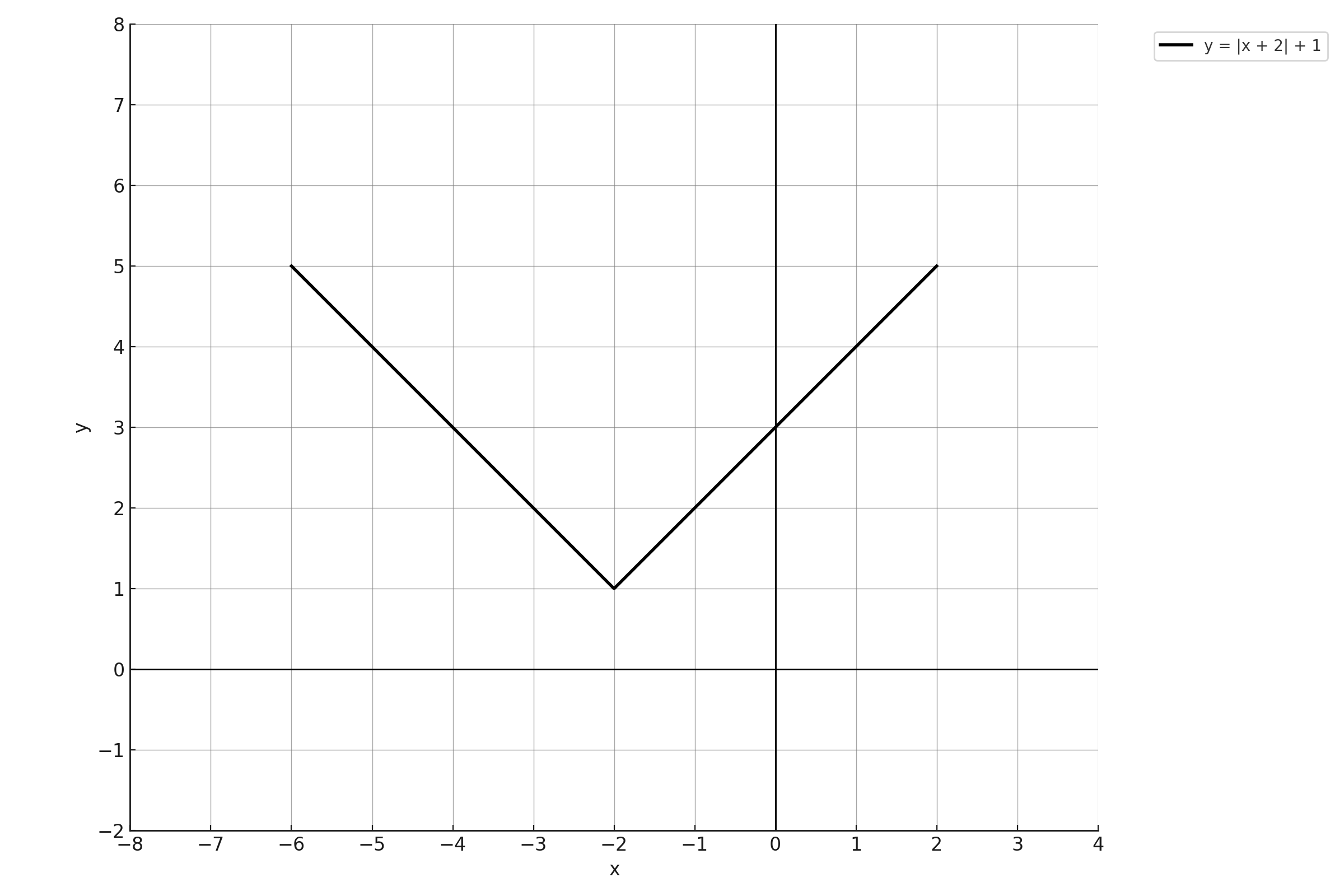
The absolute value function f is defined by an equation in the form \(\mathrm{f(x) = a|x + b| + c}\), where a, b, and c are constants. The graph of \(\mathrm{y = f(x)}\) is shown above. If \(\mathrm{g(x) = f(x - 3)}\), what is the value of \(\mathrm{a + b + c}\) for the function g?
Express your answer as an integer.
1. TRANSLATE the graph information
Looking at the graph carefully:
- The vertex (the lowest point of the V-shape) is at \(\mathrm{(-2, 1)}\)
- The function also passes through \(\mathrm{(-4, 3)}\) on the left side
- The function also passes through \(\mathrm{(0, 3)}\) on the right side
These coordinates will help us determine all the parameters.
2. INFER which parameters we can find from the vertex
Since the general form is \(\mathrm{f(x) = a|x + b| + c}\), and we know the vertex formula:
- The vertex of \(\mathrm{f(x) = a|x + b| + c}\) is at the point \(\mathrm{(-b, c)}\)
- Our vertex is at \(\mathrm{(-2, 1)}\)
- This tells us immediately:
- \(\mathrm{-b = -2}\), so \(\mathrm{b = 2}\)
- \(\mathrm{c = 1}\), so \(\mathrm{c = 1}\)
So far we have: \(\mathrm{f(x) = a|x + 2| + 1}\)
3. INFER how to find the missing parameter a
We need one more piece of information to find \(\mathrm{a}\):
- The vertex alone doesn't tell us the steepness (the value of \(\mathrm{a}\))
- We need to use another point from the graph
- Let's use the point \(\mathrm{(-4, 3)}\)
4. SIMPLIFY to find a
Substitute the point \(\mathrm{(-4, 3)}\) into \(\mathrm{f(x) = a|x + 2| + 1}\):
- \(\mathrm{f(-4) = 3}\)
- \(\mathrm{a|-4 + 2| + 1 = 3}\)
- \(\mathrm{a|-2| + 1 = 3}\)
- \(\mathrm{a(2) + 1 = 3}\)
- \(\mathrm{2a = 2}\)
- \(\mathrm{a = 1}\)
Now we have the complete function: \(\mathrm{f(x) = |x + 2| + 1}\)
5. SIMPLIFY the transformation to find g(x)
We're told that \(\mathrm{g(x) = f(x - 3)}\). This means we replace every \(\mathrm{x}\) in \(\mathrm{f(x)}\) with \(\mathrm{(x - 3)}\):
- \(\mathrm{g(x) = f(x - 3) = |(x - 3) + 2| + 1}\)
- SIMPLIFY inside the absolute value:
- \(\mathrm{(x - 3) + 2 = x - 1}\)
- So: \(\mathrm{g(x) = |x - 1| + 1}\)
6. TRANSLATE g(x) into the required form
We need to express \(\mathrm{g(x)}\) in the form \(\mathrm{a|x + b| + c}\):
- \(\mathrm{g(x) = |x - 1| + 1}\)
- Rewrite \(\mathrm{x - 1}\) as \(\mathrm{x + (-1)}\):
- \(\mathrm{g(x) = 1|x + (-1)| + 1}\)
- Therefore, for function \(\mathrm{g}\):
- \(\mathrm{a = 1}\)
- \(\mathrm{b = -1}\)
- \(\mathrm{c = 1}\)
7. Calculate the final answer
- \(\mathrm{a + b + c = 1 + (-1) + 1 = 1}\)
Answer: 1
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak SIMPLIFY skill: After finding \(\mathrm{g(x) = |x - 1| + 1}\), students incorrectly identify \(\mathrm{b = 1}\) instead of \(\mathrm{b = -1}\)
Students see \(\mathrm{|x - 1|}\) and think "the number next to x is -1, but b must be positive, so b = 1." However, they need to rewrite this in the form \(\mathrm{|x + b|}\):
- \(\mathrm{|x - 1| = |x + (-1)|}\)
- Therefore \(\mathrm{b = -1}\), not \(\mathrm{b = 1}\)
With the incorrect \(\mathrm{b = 1}\), they would calculate: \(\mathrm{a + b + c = 1 + 1 + 1 = 3}\)
This leads to an incorrect answer of 3.
Second Most Common Error:
Weak INFER skill combined with poor SIMPLIFY execution: Students confuse which parameters belong to \(\mathrm{f(x)}\) versus \(\mathrm{g(x)}\), and calculate \(\mathrm{a + b + c}\) using the original function's parameters
They correctly find that \(\mathrm{f(x) = |x + 2| + 1}\), so for \(\mathrm{f}\): \(\mathrm{a = 1, b = 2, c = 1}\)
But then they forget to apply the transformation and simply calculate: \(\mathrm{a + b + c = 1 + 2 + 1 = 4}\)
This leads to an incorrect answer of 4, using the parameters from the wrong function.
The Bottom Line:
This problem requires careful tracking of two different functions (\(\mathrm{f}\) and \(\mathrm{g}\)) and precise algebraic manipulation when rewriting expressions in standard form. The transformation \(\mathrm{f(x - 3)}\) shifts the graph but students must recognize that this changes the internal expression, affecting the value of \(\mathrm{b}\) while \(\mathrm{a}\) and \(\mathrm{c}\) remain the same in magnitude. The key pitfall is the sign: \(\mathrm{|x - 1|}\) must be rewritten as \(\mathrm{|x + (-1)|}\) to correctly identify \(\mathrm{b = -1}\).