To earn money for college, Avery works two part-time jobs: A and B. She earns $10 per hour working at...
GMAT Algebra : (Alg) Questions
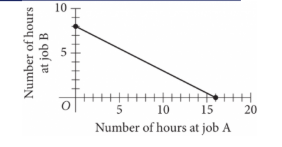
To earn money for college, Avery works two part-time jobs: A and B. She earns \(\$10\) per hour working at job A and \(\$20\) per hour working at job B. In one week, Avery earned a total of \(\mathrm{s}\) dollars for working at the two part-time jobs. The graph above represents all possible combinations of numbers of hours Avery could have worked at the two jobs to earn \(\mathrm{s}\) dollars. What is the value of \(\mathrm{s}\)?
128
160
200
320
1. TRANSLATE the problem information into an equation
- Given information:
- Job A pays \(\$10\) per hour
- Job B pays \(\$20\) per hour
- 'a' hours worked at job A
- 'b' hours worked at job B
- Total earnings = s dollars
- The earnings equation:
Total earnings = (hourly rate A × hours at A) + (hourly rate B × hours at B)
This gives us: \(\mathrm{10a + 20b = s}\)
2. TRANSLATE the graph to identify key points
The graph shows a straight line representing all combinations of hours that produce the same total earnings.
- TRANSLATE the coordinates carefully:
- The x-axis represents hours at job A
- The y-axis represents hours at job B
- Reading from the graph, two clear points on the line are:
- \(\mathrm{(16, 0)}\): 16 hours at job A, 0 hours at job B
- \(\mathrm{(0, 8)}\): 0 hours at job A, 8 hours at job B
3. INFER the solution strategy
Here's the key insight: Since all points on this line represent combinations that earn the same amount (s dollars), we can use ANY point on the line to find the value of s.
The intercepts are the easiest to read and calculate with, so let's use one of them.
4. Substitute coordinates into the equation
Using the point \(\mathrm{(16, 0)}\) where \(\mathrm{a = 16}\) and \(\mathrm{b = 0}\):
\(\mathrm{10a + 20b = s}\)
\(\mathrm{10(16) + 20(0) = s}\)
\(\mathrm{160 + 0 = s}\)
\(\mathrm{s = 160}\)
5. Verify with the other point (optional but recommended)
Using the point \(\mathrm{(0, 8)}\) where \(\mathrm{a = 0}\) and \(\mathrm{b = 8}\):
\(\mathrm{10(0) + 20(8) = s}\)
\(\mathrm{0 + 160 = s}\)
\(\mathrm{s = 160}\) ✓
Both points give us the same answer, confirming our result.
Answer: B. 160
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak TRANSLATE skill: Misreading the graph coordinates, particularly confusing which axis represents which job.
Students might read the y-intercept as \(\mathrm{(8, 0)}\) instead of \(\mathrm{(0, 8)}\), thinking "the graph reaches 8 on the axis, so that must be 8 hours at job A." When they substitute:
- \(\mathrm{10(8) + 20(0) = 80}\)
Or they might read the x-intercept incorrectly as \(\mathrm{(0, 16)}\) and calculate:
- \(\mathrm{10(0) + 20(16) = 320}\)
This may lead them to select Choice D (320) or get a value not among the choices, causing confusion and guessing.
Second Most Common Error:
Weak TRANSLATE skill combined with conceptual confusion: Mixing up the hourly rates with the job letters, or reading the wrong intercept value from the graph.
Some students might misread the y-intercept as 10 instead of 8 (perhaps confusing it with the gridline), then calculate:
- \(\mathrm{10(0) + 20(10) = 200}\)
This may lead them to select Choice C (200).
The Bottom Line:
This problem tests your ability to connect three different representations: a word problem context, an algebraic equation, and a graphical display. The critical moment is TRANSLATING the graph accurately—reading coordinates correctly and matching them to the right variables. Once you have the correct coordinates from the graph, the arithmetic is straightforward.
128
160
200
320