A research team monitored the temperature of a cooling liquid over several hours. The data collected is displayed in the...
GMAT Problem-Solving and Data Analysis : (PS_DA) Questions
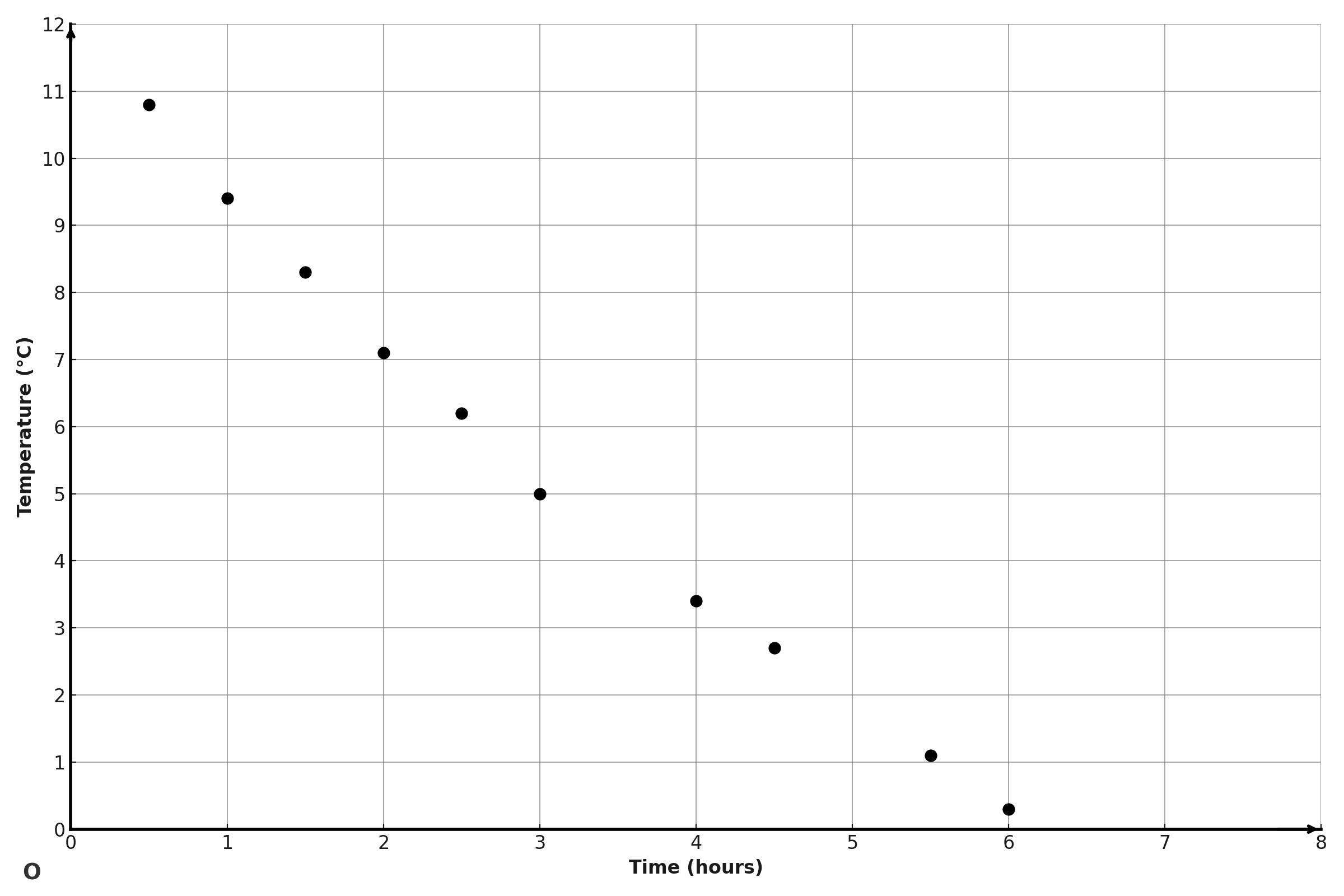
A research team monitored the temperature of a cooling liquid over several hours. The data collected is displayed in the scatterplot shown. Which of the following equations best represents the linear model for this temperature data?
\(\mathrm{T = -1.8t - 11.9}\)
\(\mathrm{T = -1.8t + 11.9}\)
\(\mathrm{T = 1.8t - 11.9}\)
\(\mathrm{T = 1.8t + 11.9}\)
1. TRANSLATE the problem information
- Given information:
- A scatterplot showing temperature (T) in °C versus time (t) in hours
- The liquid is cooling (temperature decreasing over time)
- Four possible linear equations in the form \(\mathrm{T = mt + b}\)
- What we need to find:
- Which equation best represents the data
2. INFER the direction of the relationship
- Key observation: As you scan from left to right across the scatterplot, the points move downward. This means as time increases, temperature decreases.
- Strategic reasoning: In the equation \(\mathrm{T = mt + b}\):
- If \(\mathrm{m}\) is positive, temperature increases with time
- If \(\mathrm{m}\) is negative, temperature decreases with time
- Since the liquid is cooling, we need a negative slope.
Eliminate choices C and D (both have slope +1.8)
3. INFER the y-intercept
Now we're down to:
- Choice A: \(\mathrm{T = -1.8t - 11.9}\)
- Choice B: \(\mathrm{T = -1.8t + 11.9}\)
The difference is the y-intercept (the b value).
- What does the y-intercept mean? It's the temperature at time \(\mathrm{t = 0}\) (when timing began).
- Look at the leftmost point on the scatterplot: at about \(\mathrm{t ≈ 0.5}\) hours, \(\mathrm{T ≈ 10.8°C}\)
- Think backwards: If the temperature is dropping at 1.8°C per hour, and it's 10.8°C at \(\mathrm{t = 0.5}\), then half an hour earlier:
- Temperature change = \(\mathrm{1.8 × 0.5 = 0.9°C}\) warmer
- At \(\mathrm{t = 0}\): \(\mathrm{T ≈ 10.8 + 0.9 = 11.7°C}\)
- This is close to 12°C, meaning the y-intercept must be positive (around +11.9, not -11.9)
Eliminate choice A
4. VERIFY the remaining choice
Let's check if \(\mathrm{T = -1.8t + 11.9}\) fits some data points:
- At \(\mathrm{t = 1}\): \(\mathrm{T = -1.8(1) + 11.9 = 10.1°C}\) (graph shows ≈9.4°C) ✓ Close
- At \(\mathrm{t = 3}\): \(\mathrm{T = -1.8(3) + 11.9 = 6.5°C}\) (graph shows ≈5.0°C) ✓ Close
- At \(\mathrm{t = 6}\): \(\mathrm{T = -1.8(6) + 11.9 = 1.1°C}\) (graph shows ≈0.3°C) ✓ Close
The equation provides a reasonable fit for the data.
Answer: B
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak INFER skill: Not connecting the concept of "cooling" to the sign of the slope
Some students look at the answer choices and don't immediately recognize that a cooling liquid must have a negative rate of change. They might:
- Focus only on the numbers (1.8 and 11.9) without considering signs
- Try to calculate the exact slope from two points instead of using the pattern
- Get confused by all four choices looking plausible
This leads to confusion and potentially guessing randomly among all four choices.
Second Most Common Error:
Misunderstanding y-intercept concept: Confusing the y-intercept with one of the plotted points
Students might think the y-intercept should be one of the temperatures they can see on the graph (like 10.8 at \(\mathrm{t = 0.5}\)). They fail to recognize that:
- The y-intercept occurs at \(\mathrm{t = 0}\) (off the visible data range)
- They need to extrapolate backward to find it
Without this understanding, they might select Choice A (\(\mathrm{T = -1.8t - 11.9}\)) because they correctly identify the negative slope but then guess on the y-intercept, choosing the wrong sign.
The Bottom Line:
This problem tests whether you can connect the physical situation (cooling) to mathematical properties (negative slope) and whether you understand what a y-intercept represents in context. The key is using strategic reasoning to eliminate choices systematically rather than trying to calculate everything precisely from the graph.
\(\mathrm{T = -1.8t - 11.9}\)
\(\mathrm{T = -1.8t + 11.9}\)
\(\mathrm{T = 1.8t - 11.9}\)
\(\mathrm{T = 1.8t + 11.9}\)