What is an equation of the graph shown?
GMAT Algebra : (Alg) Questions
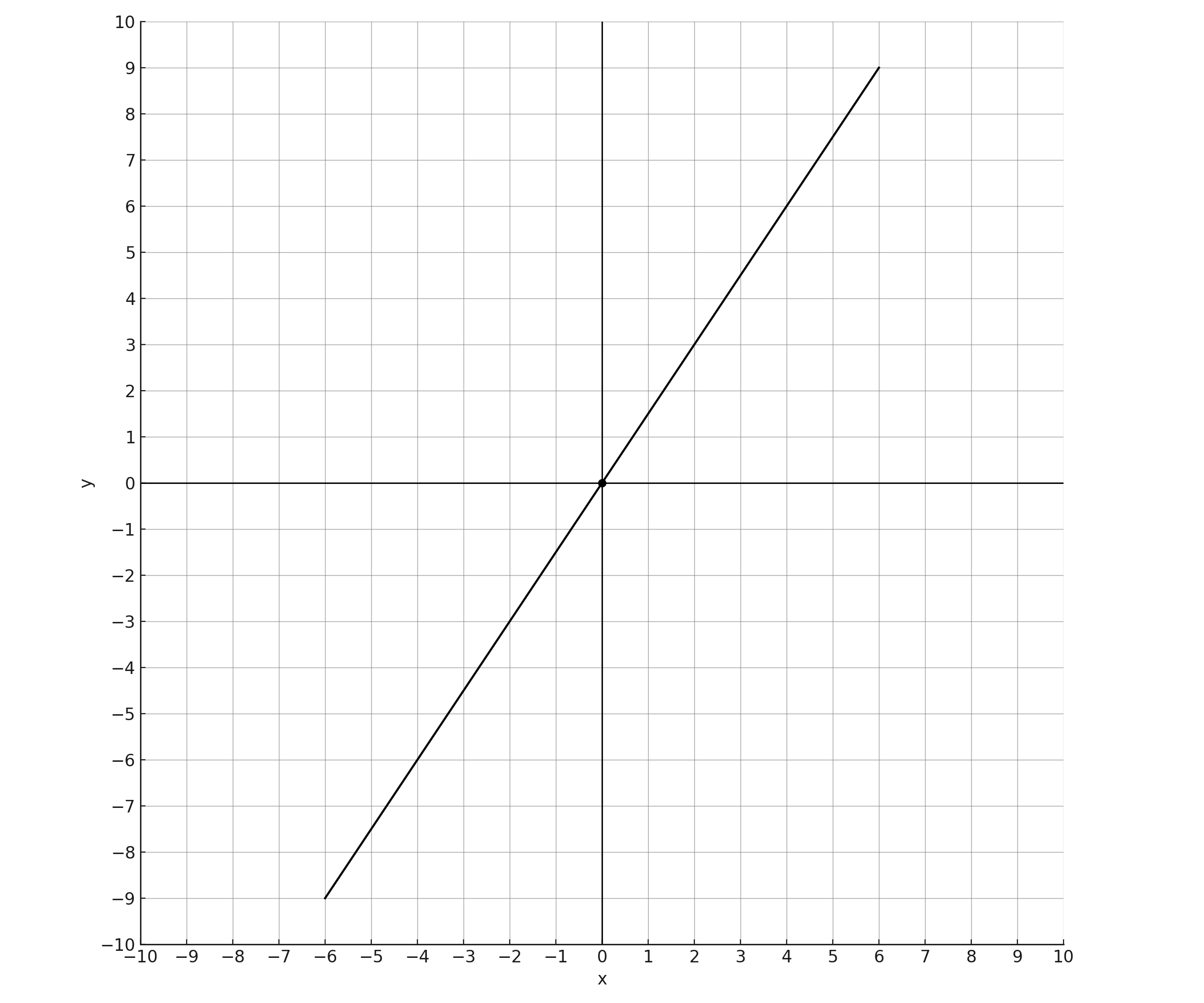
What is an equation of the graph shown?
1. TRANSLATE the graph information
Look at the graph carefully and identify at least two clear points that the line passes through:
- Point 1: The line passes through the origin (0, 0)
- Point 2: At x = 2, the line is at y = 3, giving us (2, 3)
- Point 3 (for verification): At x = -6, the line is at y = -9, giving us (-6, -9)
Key tip: Choose points where the line clearly passes through grid intersections to avoid reading errors.
2. SIMPLIFY to find the slope
Now calculate the slope using the slope formula with any two points. Let's use (0, 0) and (2, 3):
\(\mathrm{m = \frac{y_2 - y_1}{x_2 - x_1}}\)
\(\mathrm{m = \frac{3 - 0}{2 - 0}}\)
\(\mathrm{m = \frac{3}{2}}\)
3. INFER the complete equation
Since the line passes through the origin (0, 0), we know the y-intercept is 0.
Using slope-intercept form y = mx + b:
- m = 3/2 (our slope)
- b = 0 (y-intercept)
Therefore: \(\mathrm{y = \frac{3}{2}x}\)
4. Verify your answer
Always check with another point to ensure accuracy. Using (-6, -9):
\(\mathrm{y = \frac{3}{2}(-6) = -9}\) ✓
This confirms our equation is correct.
Answer: B, y = (3/2)x
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak TRANSLATE skill: Students reverse the x and y coordinates when reading from the graph, identifying the point as (3, 2) instead of (2, 3).
When they calculate the slope with this incorrect point:
\(\mathrm{m = \frac{2 - 0}{3 - 0} = \frac{2}{3}}\)
This leads them to select Choice A (y = (2/3)x) instead of the correct answer.
Prevention tip: Always read coordinates as (x, y) by first finding the x-value (horizontal position), then the y-value (vertical position). Double-check by reading multiple points.
Second Most Common Error:
Poor SIMPLIFY execution: Students make arithmetic errors when calculating the slope, especially with the division, or they mix up which difference goes in the numerator versus the denominator.
For example, calculating m = (2 - 0)/(3 - 0) = 2/3 when they had the correct points, or computing the reciprocal of the correct slope.
This may lead them to select Choice A (y = (2/3)x) or cause confusion leading to random guessing among the choices.
The Bottom Line:
This problem tests your ability to accurately extract information from a visual representation (the graph) and then apply a straightforward formula. The key challenge is precision in reading coordinates—a small mistake in identifying points cascades into selecting the wrong equation. Take your time with the graph and verify your answer with multiple points.