In the figure above, triangle ABC has side BC extended past point B. The exterior angle at B measures 110°,...
GMAT Geometry & Trigonometry : (Geo_Trig) Questions
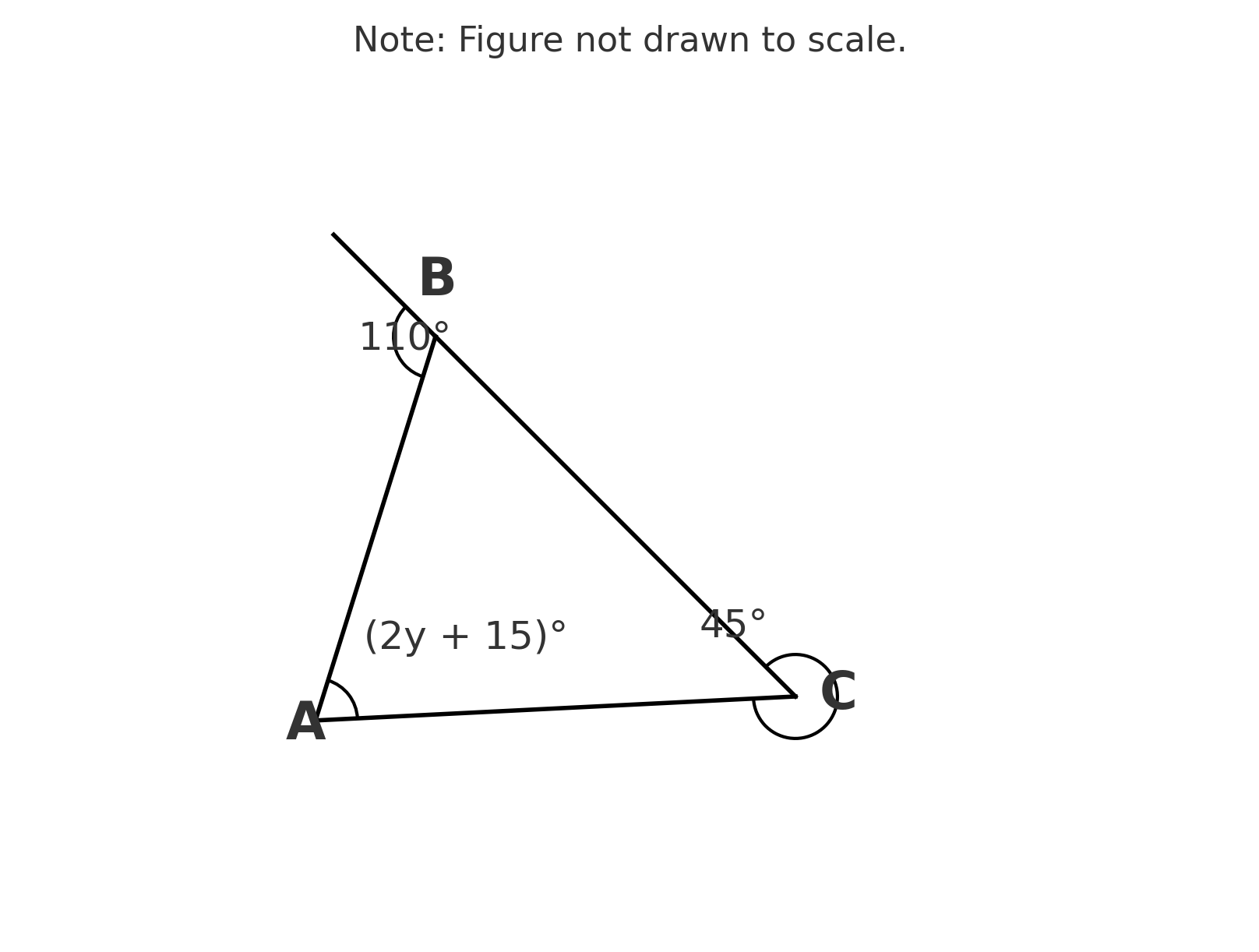
In the figure above, triangle ABC has side BC extended past point B. The exterior angle at B measures \(110°\), and angle C measures \(45°\). What is the value of \(\mathrm{y}\)?
25
40
45
60
1. TRANSLATE the diagram information into mathematical notation
From the figure, we can identify:
- Triangle ABC has an exterior angle at vertex B measuring \(110°\)
- The interior angle at C = \(45°\)
- The interior angle at A = \((2y + 15)°\)
- We need to find the value of y
Key observation: The \(110°\) angle is OUTSIDE the triangle, formed by extending side BC past point B.
2. INFER which theorem applies
When you see an exterior angle of a triangle, think: Exterior Angle Theorem
This theorem tells us that an exterior angle equals the sum of the two non-adjacent (remote) interior angles.
For the exterior angle at B:
- The two non-adjacent interior angles are angle A and angle C
- These are "non-adjacent" because they don't touch vertex B
3. TRANSLATE the theorem into an equation
Set up the relationship:
Exterior angle at B = Angle A + Angle C
\(110° = (2y + 15)° + 45°\)
4. SIMPLIFY to solve for y
Combine the constants on the right side:
\(110 = 2y + 15 + 45\)
\(110 = 2y + 60\)
Subtract 60 from both sides:
\(50 = 2y\)
Divide by 2:
\(y = 25\)
Answer: A. 25
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak INFER skill: Students don't recognize the exterior angle configuration or confuse which angles to use
Some students might see the \(110°\) angle and incorrectly think it's an interior angle of the triangle. They might then try to use the fact that all interior angles sum to \(180°\):
\(110 + 45 + (2y + 15) = 180\)
\(2y + 170 = 180\)
\(2y = 10\)
\(y = 5\)
However, 5 is not among the answer choices, which should signal that something went wrong. Students might then guess randomly or select Choice (A) (25) by chance without understanding why.
Second Most Common Error:
Poor SIMPLIFY execution: Arithmetic mistakes when combining terms
Students correctly set up the equation \(110 = (2y + 15) + 45\), but then make calculation errors:
- Adding \(15 + 45\) incorrectly (getting 50 instead of 60)
- Making sign errors when isolating the variable
For example, if they incorrectly compute \(15 + 45 = 50\):
\(110 = 2y + 50\)
\(60 = 2y\)
\(y = 30\)
Since 30 isn't an answer choice, this leads to confusion and guessing.
The Bottom Line:
This problem requires solid recognition of exterior angle configurations in triangle diagrams. The key insight is identifying that the \(110°\) angle is OUTSIDE the triangle and therefore uses the Exterior Angle Theorem rather than the interior angle sum property. Once you have the correct theorem, it's just straightforward algebra.
25
40
45
60