Note: Figure not drawn to scale.In the figure, line m is parallel to line n, and line k intersects both...
GMAT Geometry & Trigonometry : (Geo_Trig) Questions
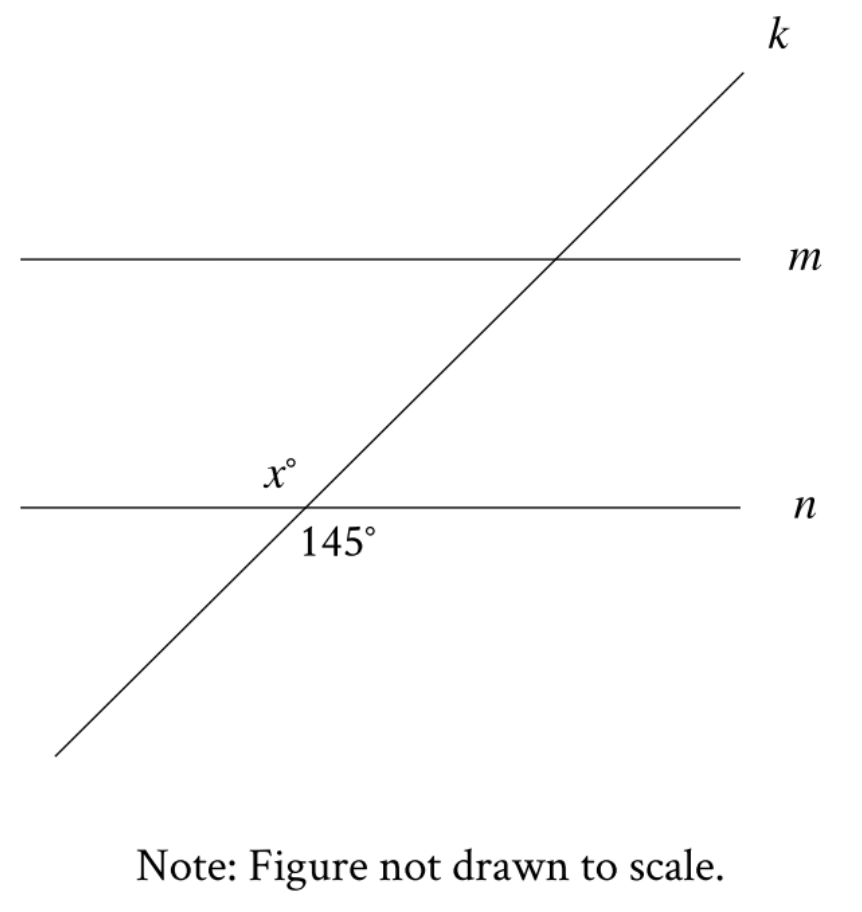
Note: Figure not drawn to scale.
In the figure, line m is parallel to line n, and line k intersects both lines. Which of the following statements is true?
1. VISUALIZE the angle relationships in the diagram
Look carefully at where line k intersects line n:
- There's an angle marked \(x°\) on one side of the intersection
- There's an angle marked \(145°\) on the opposite side of the intersection
- These two angles are across from each other at the intersection point
What this tells us: When you have two angles on opposite sides of an intersection point, they are called vertical angles.
2. INFER which geometric property applies
Now that we've identified \(x°\) and \(145°\) as vertical angles, we need to recall what we know about them:
- Vertical angles are always congruent (they have the same measure)
- This is a fundamental property that's always true when two lines intersect
Strategic decision: We don't need to use the parallel lines information at all! The fact that m ∥ n is given, but the problem is really about the single intersection point where k crosses n.
3. Apply the vertical angles property
Since vertical angles are congruent:
\(x° = 145°\)
Therefore: x = 145
Answer: C. The value of x is equal to 145.
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak VISUALIZE skill: Students see two angles at an intersection and assume they must be supplementary (add to 180°) because they appear to be next to each other on a line.
If a student thinks x and 145 are supplementary angles (a linear pair):
- They would set up: \(x + 145 = 180\)
- Solving: \(x = 35\)
This may lead them to select Choice A (The value of x is less than 145) since 35 < 145.
Second Most Common Error:
Poor INFER reasoning: Students see that the problem mentions parallel lines and think they must use properties of parallel lines cut by a transversal (like corresponding angles, alternate interior angles, etc.).
This causes confusion because:
- They try to find relationships between angles at different intersection points
- They get distracted by the parallel lines information
- They can't identify which parallel line property to apply
This leads to confusion and guessing among the answer choices, or possibly selecting Choice D (The value of x cannot be determined) because they feel they don't have enough information.
The Bottom Line:
This problem tests whether you can correctly identify angle relationships in a diagram. The mention of parallel lines is a distractor—the solution only requires recognizing vertical angles at a single intersection point. Students who carefully VISUALIZE the specific angles marked in the diagram and correctly identify them as vertical angles will solve this quickly and confidently.