In the figure, lines k and ℓ are parallel and a transversal r intersects both. The angle formed at line...
GMAT Geometry & Trigonometry : (Geo_Trig) Questions
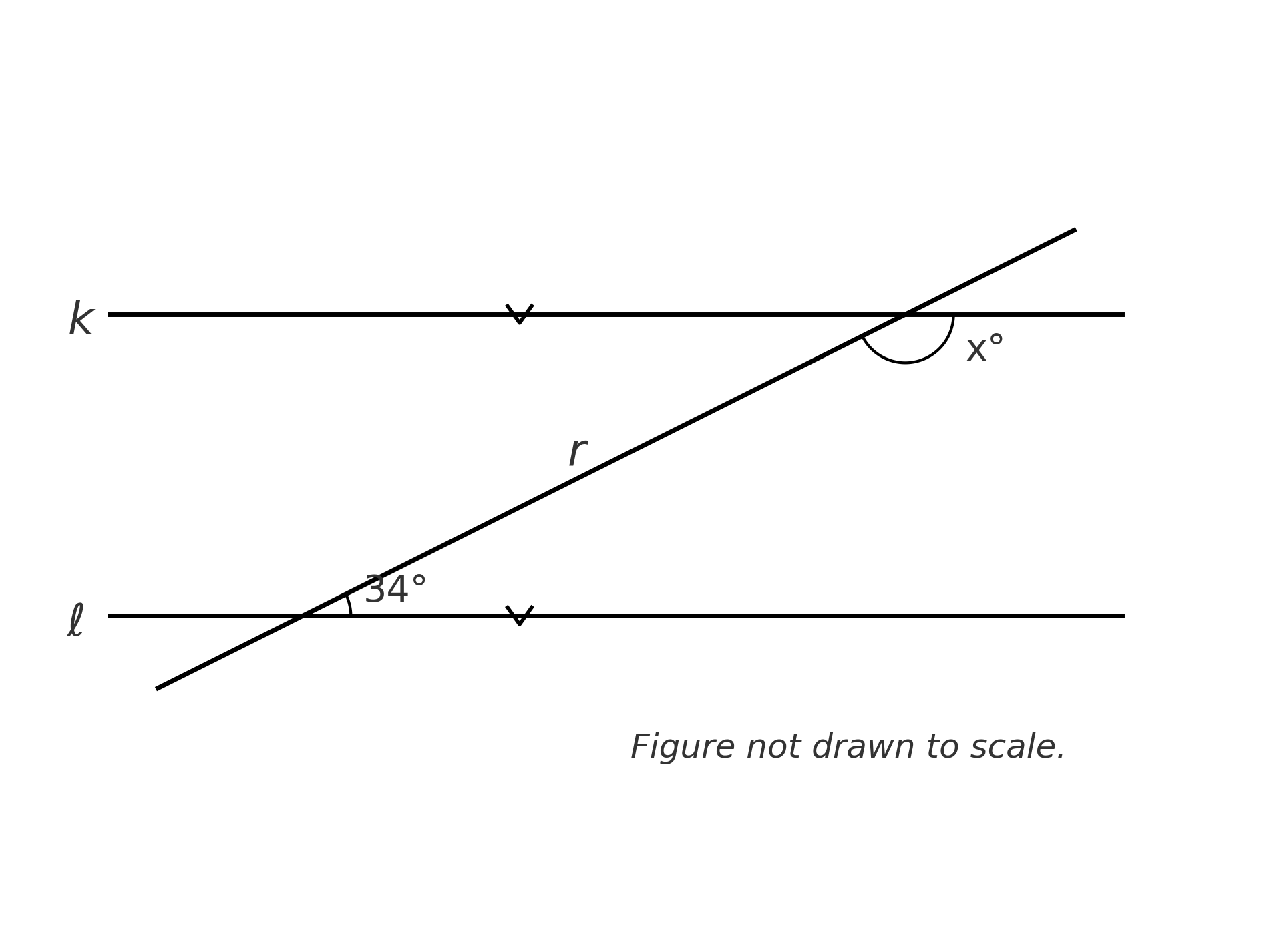
In the figure, lines k and ℓ are parallel and a transversal r intersects both. The angle formed at line ℓ that lies above ℓ and to the right of r measures 34°. At line k, the angle that lies below k and to the right of r is labeled x°. What is the value of x? (Note: Figure not drawn to scale.)
34
68
112
146
1. TRANSLATE the problem information
- Given facts:
- Lines k and ℓ are parallel (marked with arrows in the figure)
- Transversal line r crosses both parallel lines
- At line ℓ: the angle above the line and to the right of r = \(34°\)
- At line k: the angle below the line and to the right of r = \(x°\)
- What we need to find: The value of x
2. INFER which angle relationship to use
This is the crucial strategic step. We need to identify what type of angle pair these two angles form.
- Position analysis:
- Both angles are between the two parallel lines (making them interior angles)
- Both angles are on the same side of the transversal r (both to the right)
- One is above its line, one is below its line
- Angle relationship: These are consecutive interior angles (also called same-side interior angles or co-interior angles)
- Key property: When parallel lines are cut by a transversal, consecutive interior angles are always supplementary—they add up to \(180°\)
3. Set up the equation
Since consecutive interior angles are supplementary:
\(34° + x° = 180°\)
4. SIMPLIFY to solve for x
\(x = 180° - 34°\)
\(x = 146°\)
Answer: D (146)
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
INFER - Confusing angle relationships: Students often mix up consecutive interior angles with alternate interior angles. Alternate interior angles (which are on opposite sides of the transversal and both between the parallel lines) are congruent, not supplementary.
If a student thinks these are alternate interior angles (or corresponding angles, which are also congruent), they would conclude that \(x = 34\).
This leads them to select Choice A (34).
Second Most Common Error:
TRANSLATE - Misidentifying angle positions: The verbal description requires careful attention. Students may misidentify which angles are being referenced, especially if they don't carefully track "above ℓ" vs "below k" and "to the right of r" in both cases. This spatial confusion can lead them to identify the wrong pair of angles or the wrong relationship.
This causes them to get stuck and guess, or potentially arrive at an incorrect angle relationship.
The Bottom Line:
This problem tests whether students can both accurately identify angle positions from verbal descriptions AND correctly recall which angle relationship applies. The key challenge is distinguishing consecutive interior angles (supplementary) from alternate interior angles (congruent)—two relationships that students frequently confuse because both involve "interior" angles formed by parallel lines and a transversal.
34
68
112
146