In the coordinate plane shown, the graphs of two linear equations intersect at a single point. What is the solution...
GMAT Algebra : (Alg) Questions
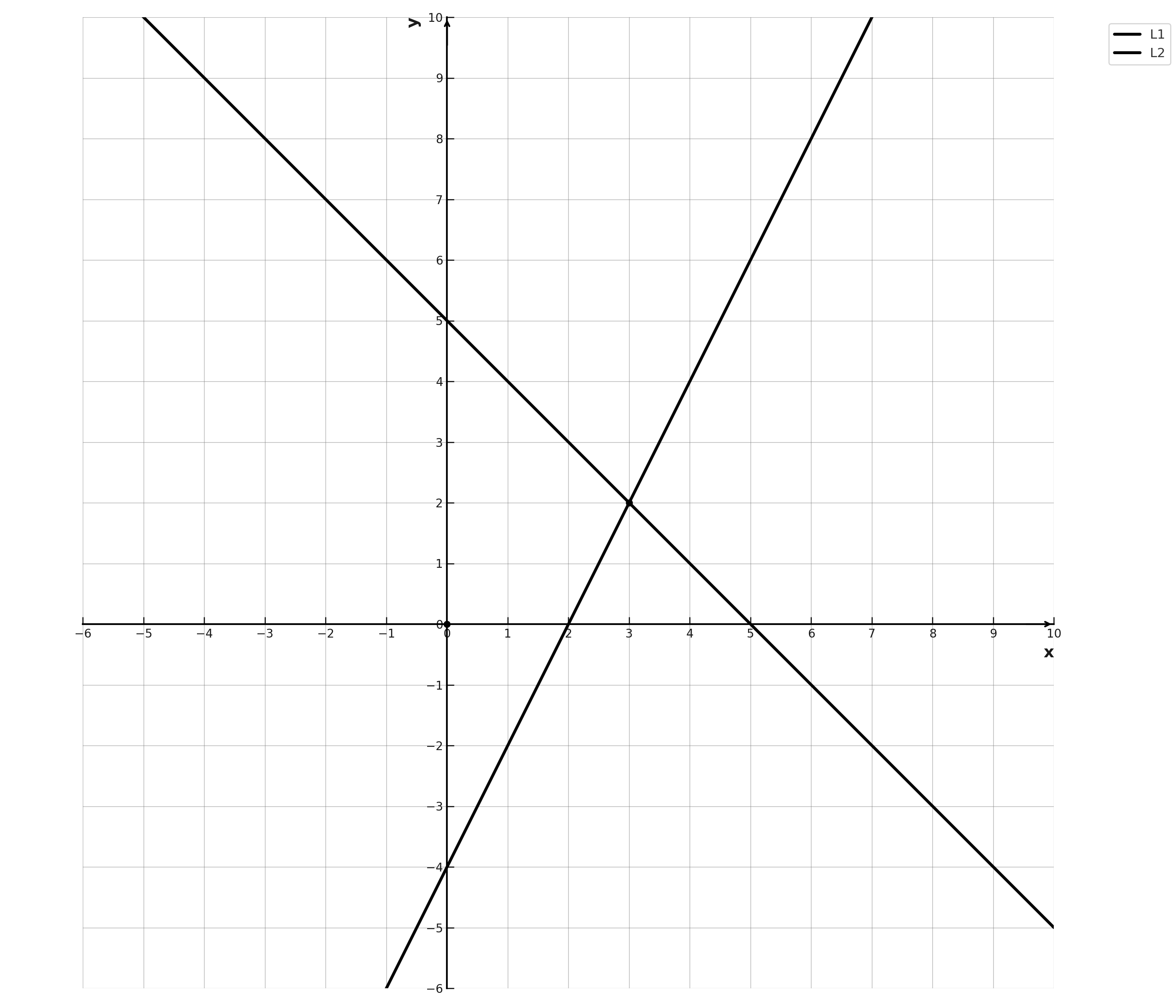
In the coordinate plane shown, the graphs of two linear equations intersect at a single point. What is the solution \(\mathrm{(x, y)}\) to the system represented by the two lines?
\((2, 3)\)
\((3, 2)\)
\((5, 0)\)
\((0, 5)\)
1. INFER what the problem is asking
The problem asks for the solution to a system of linear equations. The key insight here is that when two lines are graphed on the same coordinate plane, their solution is the point where they intersect - the \(\mathrm{(x, y)}\) coordinates that satisfy both equations simultaneously.
2. TRANSLATE the graph to identify the intersection point
Looking at the graph:
- Line L1 (decreasing from upper left to lower right)
- Line L2 (increasing from lower left to upper right)
- The two lines cross at exactly one point
Locate where the lines intersect:
- Follow line L1 and line L2 until they meet
- The intersection occurs at a lattice point (a point where grid lines cross)
- Reading the coordinates carefully: moving right 3 units from the origin (\(\mathrm{x} = 3\)) and up 2 units (\(\mathrm{y} = 2\))
The intersection point is \((3, 2)\).
3. APPLY CONSTRAINTS to verify the answer
Check that this point makes sense:
- The x-coordinate is 3 (the horizontal position)
- The y-coordinate is 2 (the vertical position)
- This matches answer choice (B): \((3, 2)\)
Answer: (B) \((3, 2)\)
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak TRANSLATE skill: Reversing the order of coordinates
Students sometimes confuse which coordinate comes first. They correctly identify the intersection point on the graph but write the coordinates in the wrong order - putting the y-value first and the x-value second.
If a student sees the point is at "horizontal position 3, vertical position 2" but writes it as \((2, 3)\) instead of \((3, 2)\), they would select Choice A: \((2, 3)\).
Second Most Common Error:
Weak TRANSLATE skill: Misreading the grid or identifying the wrong point
When reading graphs quickly, students may:
- Read coordinates of one of the y-intercepts or x-intercepts instead of the intersection point
- Miscount the grid lines
- Focus on point \((0, 5)\) where L1 crosses the y-axis, leading them to select Choice D: \((0, 5)\)
- Focus on point \((5, 0)\) where L1 crosses the x-axis, leading them to select Choice C: \((5, 0)\)
The Bottom Line:
This problem primarily tests careful graph reading. The concept (that the solution is where lines intersect) is straightforward, but precision matters. Take your time to correctly identify which point is the intersection and remember that coordinates are always written as \(\mathrm{(x, y)}\) - horizontal position first, then vertical position.
\((2, 3)\)
\((3, 2)\)
\((5, 0)\)
\((0, 5)\)