In the figure, two lines intersect at a point. Angle 1 and Angle 2 are vertical angles. The measure of...
GMAT Geometry & Trigonometry : (Geo_Trig) Questions
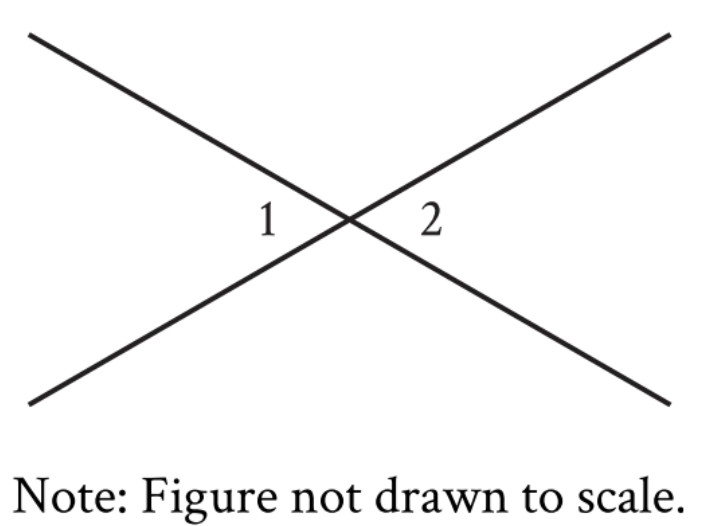
In the figure, two lines intersect at a point. \(\mathrm{Angle\ 1}\) and \(\mathrm{Angle\ 2}\) are vertical angles. The measure of \(\mathrm{Angle\ 1}\) is \(72°\). What is the measure of \(\mathrm{Angle\ 2}\)?
1. TRANSLATE the problem information
- Given information:
- Two lines intersect at a point
- Angle 1 and angle 2 are vertical angles
- Measure of angle 1 = \(72°\)
- What we need to find:
- Measure of angle 2
2. INFER what property applies
- The problem tells us that angles 1 and 2 are vertical angles. This is the crucial piece of information.
- When two lines intersect, they form four angles at the intersection point. The angles directly across from each other (opposite sides of the intersection) are called vertical angles.
- Key property to apply: Vertical angles are always congruent, meaning they have equal measures.
3. Apply the vertical angles property
- Since angle 1 and angle 2 are vertical angles, they must be equal in measure.
- Therefore: measure of angle 2 = measure of angle 1 = \(72°\)
Answer: A. 72°
Why Students Usually Falter on This Problem
Most Common Error Path:
Weak INFER skill - Confusing vertical angles with supplementary angles:
Students sometimes confuse the relationship between vertical angles with the relationship between supplementary angles. When two lines intersect, adjacent angles (angles that share a side) are supplementary, meaning they add up to 180°.
A student might mistakenly think: "Angle 1 and angle 2 must add to 180° because they're formed by intersecting lines." This leads to the calculation:
- Angle 2 = \(180° - 72°\)
- \(= 108°\)
This may lead them to select Choice B (108°).
Second Most Common Error:
Weak INFER skill - Adding angles instead of recognizing congruence:
Some students might think they need to perform an operation with both angles rather than recognizing they're equal. They might incorrectly add angle 1 to itself or add both angles together:
- \(72° + 72°\)
- \(= 144°\)
This may lead them to select Choice C (144°).
The Bottom Line:
The key to this problem is recognizing and correctly applying the vertical angles property. Students must distinguish between vertical angles (which are equal) and supplementary angles (which add to 180°). This is a fundamental geometry concept that appears frequently, so understanding the distinction is crucial.