Flint artifacts dating to 800,000 to 1,000,000 years ago have been recovered from the Evron Quarry in Israel. Likely created...
GMAT Information and Ideas : (Ideas) Questions
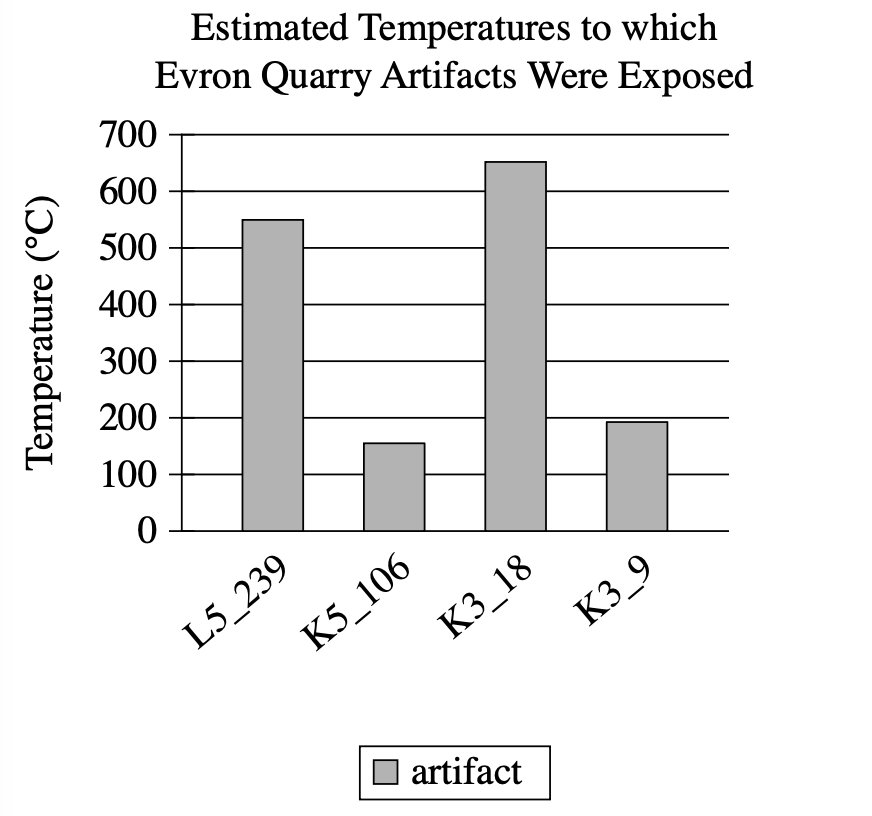
Flint artifacts dating to \(\mathrm{800,000\ to\ 1,000,000}\) years ago have been recovered from the Evron Quarry in Israel. Likely created by the hominin Homo erectus, the artifacts have no visual features suggesting that they were exposed to fire, leading some scholars to conclude that these hominins had not acquired control of fire. But Zane Stepka and colleagues recently used a new method to determine whether these artifacts had been exposed to temperatures above \(\mathrm{400°C}\) (the typical temperature campfires reach) and concluded that the hominins who inhabited the site may have had control of fire.
Which choice best describes data in the graph that support the team's conclusion?
Artifacts K5_106 and K3_9 were exposed to temperatures above 400°C.
Artifacts L5_239 and K3_18 were exposed to temperatures of approximately 550°C and 650°C, respectively.
All of the artifacts were exposed to temperatures above 100°C.
Artifact K3_9 was exposed to a higher temperature than was artifact K5_106.
Step 1: Decode and Map All Source Material
Passage Analysis Table
| Text from Passage | Analysis |
|---|---|
| "Flint artifacts dating to 800,000 to 1,000,000 years ago have been recovered from the Evron Quarry in Israel." |
|
| "Likely created by the hominin Homo erectus, the artifacts have no visual features suggesting that they were exposed to fire, leading some scholars to conclude that these hominins had not acquired control of fire." |
|
| "But Zane Stepka and colleagues recently used a new method to determine whether these artifacts had been exposed to temperatures above 400°C (the typical temperature campfires reach)" |
|
| "and concluded that the hominins who inhabited the site may have had control of fire." |
|
Visual Data Analysis

Visual Type & Title: Bar chart titled "Estimated Temperatures to which Evron Quarry Artifacts Were Exposed"
What It Shows: Y-axis shows Temperature in °C (0-700), X-axis shows 4 artifacts (L5_239, K5_106, K3_18, K3_9), displays estimated exposure temperatures for each artifact with key data: L5_239 approximately 550°C, K5_106 approximately 160°C, K3_18 approximately 650°C, K3_9 approximately 190°C
Key Observations: 2 artifacts exceed 400°C: L5_239 (approximately 550°C), K3_18 (approximately 650°C); 2 artifacts below 400°C: K5_106 (approximately 160°C), K3_9 (approximately 190°C); Wide temperature range (160-650°C); L5_239 & K3_18 well above campfire threshold (400°C)
Connection to Text: The graph provides the quantitative evidence that Stepka's team used to support their conclusion about possible fire control - specifically showing which artifacts were exposed to campfire-level temperatures.
Passage Architecture & Core Elements
Main Point: New temperature-testing methods suggest that some artifacts from Evron Quarry were exposed to campfire-level heat, challenging the traditional view that these ancient hominins lacked fire control.
Argument Flow: The passage moves from established archaeological context to a scholarly disagreement: traditional visual analysis suggested no fire use, but new temperature-testing methods provide evidence that some artifacts were heated to campfire temperatures, supporting the possibility of fire control.
Text-Visual Synthesis: The graph provides the specific quantitative evidence underlying Stepka's team's conclusion—while the text explains that they tested for exposure above 400°C (campfire temperature), the graph shows that two artifacts (L5_239 and K3_18) indeed reached approximately 550°C and 650°C respectively, well above the campfire threshold.
Step 2: Interpret the Question Precisely
What's being asked? Which choice best describes data in the graph that support the team's conclusion?
What type of answer do we need? Specific graph data that provides evidence for Stepka's team's conclusion about possible fire control
Any limiting keywords? "data in the graph" - we must focus on what the visual shows, not just text information; "support the team's conclusion" - we need data that backs up their claim about fire control
Step 3: Prethink the Answer
- The team's conclusion is that these hominins "may have had control of fire"
- This conclusion is based on finding artifacts exposed to temperatures above 400°C, which is the typical campfire temperature mentioned in the text
- To support this conclusion, the correct answer should:
- Reference specific artifacts that were exposed to temperatures above 400°C
- Provide the actual temperature values from the graph
- Show that at least some artifacts reached campfire-level heat (400°C+)
- From the graph, L5_239 (approximately 550°C) and K3_18 (approximately 650°C) are the two artifacts that clearly exceed the 400°C campfire threshold, while K5_106 (approximately 160°C) and K3_9 (approximately 190°C) fall well below it
- So the right answer should identify L5_239 and K3_18 as being exposed to temperatures around 550°C and 650°C respectively, demonstrating evidence for fire control
Artifacts K5_106 and K3_9 were exposed to temperatures above 400°C.
- States that K5106 and K39 were exposed to temperatures above \(400°\mathrm{C}\)
- This contradicts the graph data: K5106 shows approximately \(160°\mathrm{C}\) and K39 shows approximately \(190°\mathrm{C}\)
- Both are well below the \(400°\mathrm{C}\) campfire threshold, so this wouldn't support fire control
Artifacts L5_239 and K3_18 were exposed to temperatures of approximately 550°C and 650°C, respectively.
- Accurately describes the graph data: L5239 at approximately \(550°\mathrm{C}\) and K318 at approximately \(650°\mathrm{C}\)
- Both temperatures are well above the \(400°\mathrm{C}\) campfire threshold mentioned in the text
- This directly supports the team's conclusion about possible fire control since these artifacts were exposed to campfire-level temperatures
All of the artifacts were exposed to temperatures above 100°C.
- While all artifacts appear to be above \(100°\mathrm{C}\) according to the graph, this is irrelevant to the team's conclusion
- The critical threshold is \(400°\mathrm{C}\) (campfire temperature), not \(100°\mathrm{C}\)
- Exposure above \(100°\mathrm{C}\) doesn't indicate fire control, so this data doesn't support their conclusion
Artifact K3_9 was exposed to a higher temperature than was artifact K5_106.
- While K39 (approximately \(190°\mathrm{C}\)) was exposed to higher temperature than K5106 (approximately \(160°\mathrm{C}\)), this comparison is irrelevant
- Neither artifact reached the critical \(400°\mathrm{C}\) campfire threshold
- A relative comparison between two low temperatures doesn't support the fire control conclusion