In a study of the evolution of DptA and DptB—Diptericin genes encoding antimicrobial peptides that combat pathogens and foster beneficial...
GMAT Information and Ideas : (Ideas) Questions
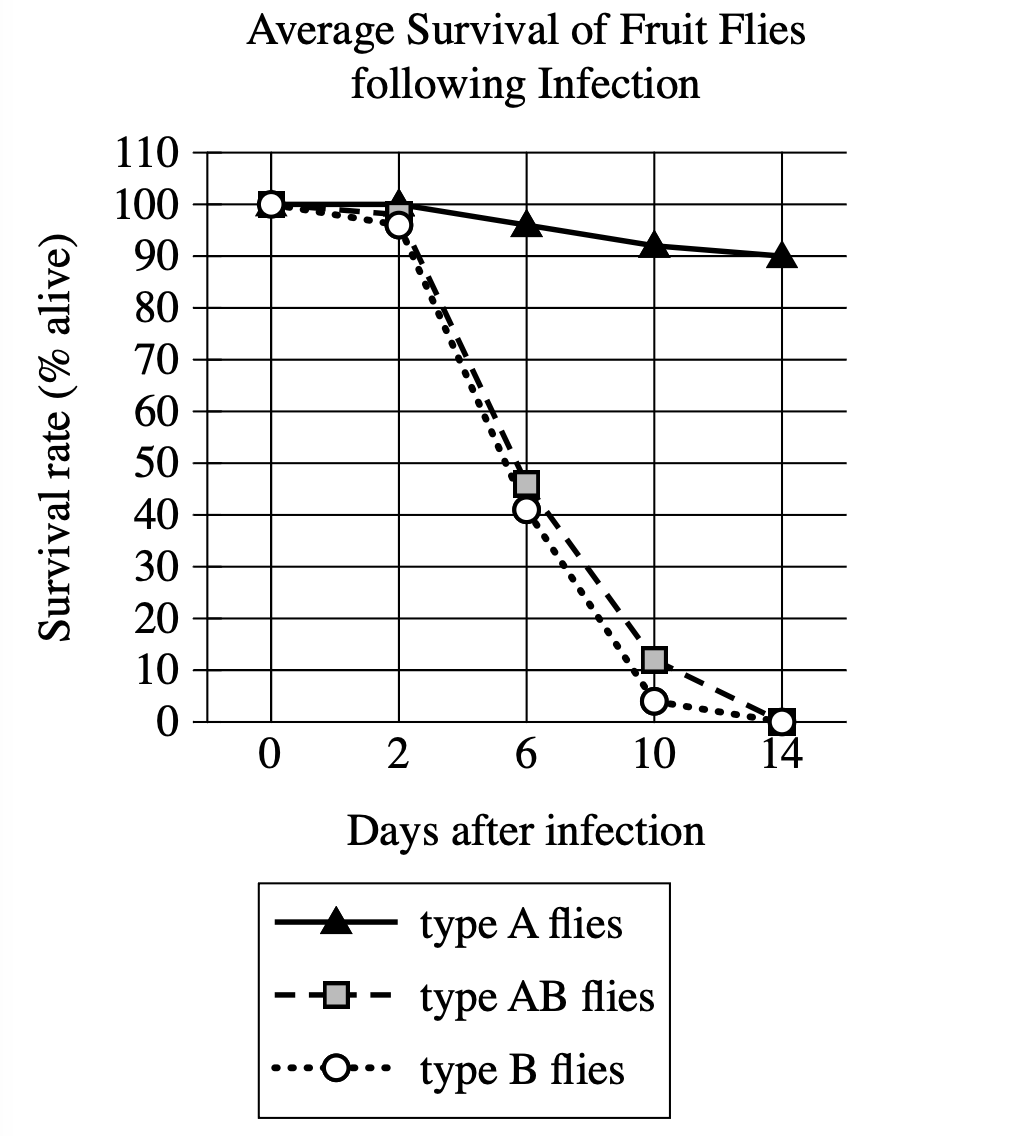
In a study of the evolution of DptA and DptB—Diptericin genes encoding antimicrobial peptides that combat pathogens and foster beneficial microbes in fruit flies (Drosophila)—researchers assessed Drosophila melanogaster resistance to pathogenic infections by Providencia rettgeri and Acetobacter sicerae, bacteria common in the flies' environments. Subjects included flies identified by mutations silencing DptA, DptB, or both DptA and DptB (termed types A, B, and AB, respectively). In conjunction with the observation that resistance to P. rettgeri correlates with DptA activity but is not significantly affected by DptB activity, data in the graph of survival rates post–A. sicerae infection suggest that ______.
Which completion of the text is best supported by data in the graph?
DptA confers defense against A. sicerae regardless of the presence of DptB.
DptB protects against only one bacteria species, whereas DptA protects against multiple species.
DptB may have developed as a specific defense against A. sicerae.
defense against A. sicerae is strongest when both DptA and DptB are present.
Step 1: Decode and Map All Source Material
Part A: Passage Analysis Table
| Text from Passage | Analysis |
|---|---|
| "In a study of the evolution of DptA and DptB—Diptericin genes encoding antimicrobial peptides that combat pathogens and foster beneficial microbes in fruit flies (Drosophila)" |
|
| "researchers assessed Drosophila melanogaster resistance to pathogenic infections by Providencia rettgeri and Acetobacter sicerae, bacteria common in the flies' environments" |
|
| "Subjects included flies identified by mutations silencing DptA, DptB, or both DptA and DptB (termed types A, B, and AB, respectively)" |
|
| "In conjunction with the observation that resistance to P. rettgeri correlates with DptA activity but is not significantly affected by DptB activity" |
|
| "data in the graph of survival rates post–A. sicerae infection suggest that ______" |
|
Visual Data Analysis

Visual Type & Title: Line graph - "Average Survival of Fruit Flies following Infection"
What It Shows:
- X-axis: Days after infection (0-14)
- Y-axis: Survival rate (% alive, 0-110%)
- 3 lines: Type A flies (solid w/ triangles), Type AB flies (dashed w/ squares), Type B flies (dotted w/ circles)
- Tracks survival over 14 days post-A. sicerae infection
Key Observations:
- Type A flies (DptB only): gradual decline 100%→90% (best survival)
- Type B flies (DptA only): rapid decline 100%→3% by day 14 (poor survival)
- Type AB flies (neither): rapid decline 100%→near 0% by day 14 (poor survival)
- Type B ≈ Type AB performance (both poor vs A. sicerae)
- Only Type A maintains good survival rates
Part B: Passage Architecture & Core Elements
Main Point: Researchers studied fruit flies with different gene mutations to understand how DptA and DptB genes defend against different bacterial infections.
Text-Visual Synthesis: The text establishes that DptA protects against P. rettgeri while DptB doesn't, but the graph reveals the opposite pattern for A. sicerae—Type A flies (DptB only) survive well while Type B flies (DptA only) perform poorly. This suggests different genes specialize against different bacterial threats.
Step 2: Interpret the Question Precisely
This is a fill-in-the-blank question asking us to choose the best logical connector. The answer must create the right relationship between what comes before and after the blank.
Step 3: Prethink the Answer
- From the graph, we can see that Type A flies (which only have DptB active) survive A. sicerae infection much better than Type B flies (which only have DptA active)
- Type B flies perform almost as poorly as Type AB flies (which have neither gene active)
- This creates a clear pattern: DptB seems crucial for A. sicerae defense, while DptA doesn't help much against A. sicerae
- Combined with the text telling us that DptA (not DptB) helps against P. rettgeri, this suggests the genes have specialized functions - each defending against different bacterial threats
DptA confers defense against A. sicerae regardless of the presence of DptB.
✗ Incorrect
- Claims DptA protects against A. sicerae regardless of DptB presence
- Graph shows Type B flies (DptA only) perform terribly - similar to Type AB flies (neither gene)
- Contradicts the clear visual evidence that DptA alone doesn't help against A. sicerae
DptB protects against only one bacteria species, whereas DptA protects against multiple species.
✗ Incorrect
- Claims DptB protects against only one species while DptA protects against multiple
- We only have data on two species total - can't conclude DptA protects against 'multiple' species
- Graph shows DptA doesn't even protect against A. sicerae
DptB may have developed as a specific defense against A. sicerae.
✓ Correct
- Suggests DptB developed as specific defense against A. sicerae
- Graph shows Type A flies (DptB only) maintain ~90% survival while Types B and AB (no DptB) drop to nearly 0%
- Perfectly matches the pattern where DptB presence correlates with A. sicerae survival
defense against A. sicerae is strongest when both DptA and DptB are present.
✗ Incorrect
- Claims defense is strongest when both genes are present
- We have no data on flies with both genes active (our flies have one or both silenced)
- Graph only shows flies missing at least one gene, so can't support this claim