In tomato plants, herbivory induces defensive production of jasmonic acid, while microbial infection induces defensive production of salicylic acid; p...
GMAT Information and Ideas : (Ideas) Questions
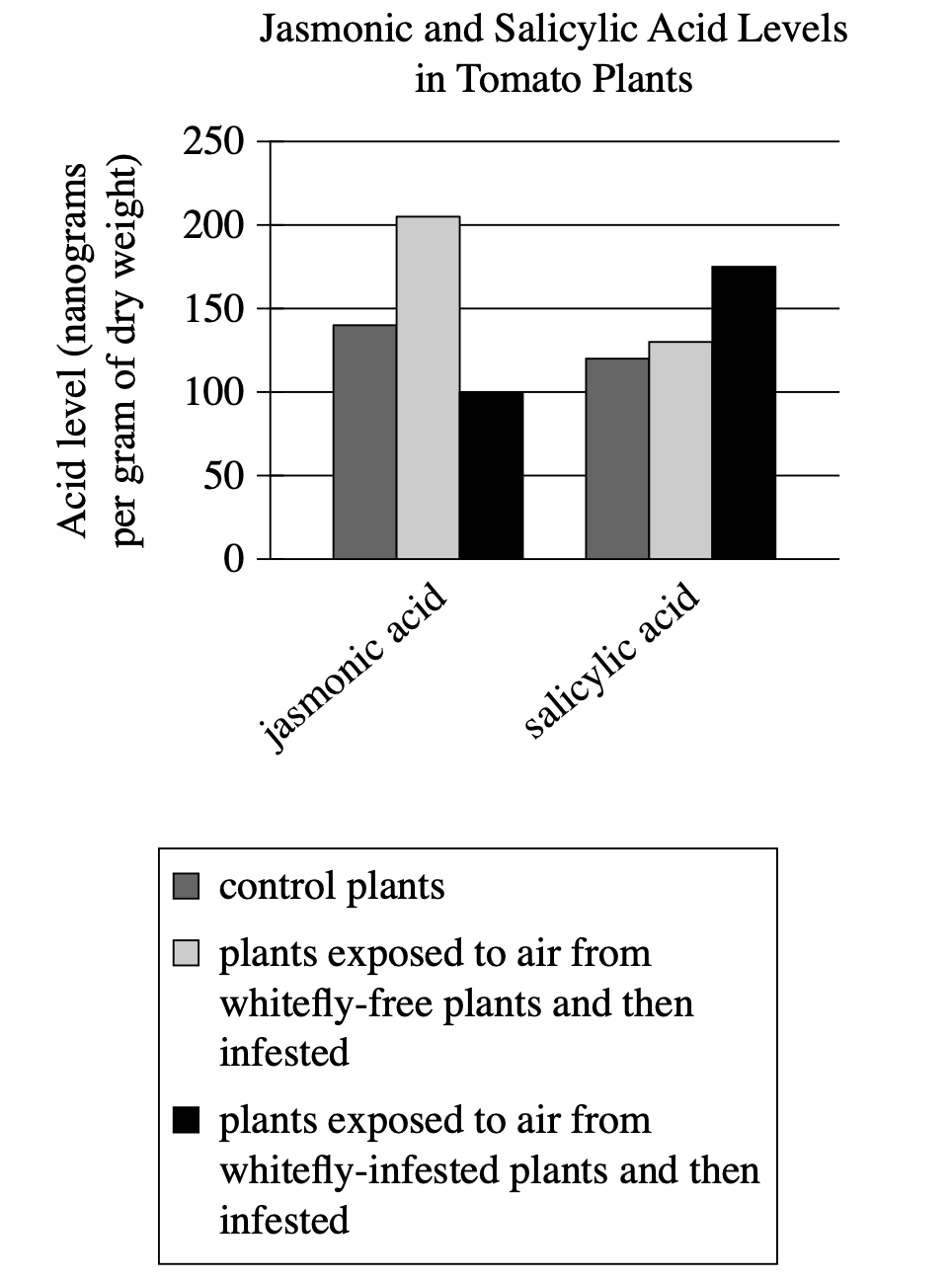
In tomato plants, herbivory induces defensive production of jasmonic acid, while microbial infection induces defensive production of salicylic acid; plants also emit airborne chemicals to initiate the appropriate defense in nearby tomato plants. Researchers investigated the poor resistance tomato plants show to whitefly herbivory by exposing some plants to airborne chemicals from whitefly-free plants and others to airborne chemicals from whitefly-infested plants, then infesting both groups of plants with whiteflies. The researchers concluded that whiteflies induce tomato plants to emit chemicals that cause other tomato plants to preferentially defend against microbial infection even when under herbivorous attack.
Which choice best describes data from the graph that support the researchers' conclusion?
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced more jasmonic acid than did control plants, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they produced less jasmonic acid and more salicylic acid than did control plants.
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they produced less jasmonic acid than salicylic acid, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced about the same amount of jasmonic acid and salicylic acid.
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced both jasmonic acid and salicylic acid, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they exclusively produced salicylic acid.
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they produced less jasmonic acid than did control plants, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced more jasmonic acid and salicylic acid than did control plants.
Step 1: Decode and Map All Source Material
Part A: Create Passage Analysis Table
| Text from Passage | Analysis |
|---|---|
| "In tomato plants, herbivory induces defensive production of jasmonic acid, while microbial infection induces defensive production of salicylic acid" |
|
| "plants also emit airborne chemicals to initiate the appropriate defense in nearby tomato plants" |
|
| "Researchers investigated the poor resistance tomato plants show to whitefly herbivory by exposing some plants to airborne chemicals from whitefly-free plants and others to airborne chemicals from whitefly-infested plants, then infesting both groups of plants with whiteflies" |
|
| "The researchers concluded that whiteflies induce tomato plants to emit chemicals that cause other tomato plants to preferentially defend against microbial infection even when under herbivorous attack" |
|
Visual Data Analysis

Visual Type & Title: Bar chart - "Jasmonic and Salicylic Acid Levels in Tomato Plants"
What It Shows:
- Y-axis: Acid level (nanograms per gram dry weight), 0-250 range
- Two acid types: jasmonic acid, salicylic acid
- Three plant groups: control, exposed to whitefly-free air, exposed to whitefly-infested air
- Units: ng/g dry weight
Key Observations:
- Control plants: ~140 jasmonic, ~120 salicylic (jasmonic > salicylic)
- Whitefly-free air exposure: ~205 jasmonic, ~130 salicylic (jasmonic >> salicylic)
- Whitefly-infested air exposure: ~100 jasmonic, ~175 salicylic (salicylic > jasmonic)
- Pattern reversal: whitefly-infested air → ↓jasmonic, ↑salicylic vs controls
Connection to Text: Graph provides quantitative evidence for researchers' conclusion that whitefly-infested plants emit chemicals causing preferential microbial defense (more salicylic acid) in nearby plants.
Part B: Provide Passage Architecture & Core Elements
Main Point: Researchers found that whiteflies cause tomato plants to send chemical signals that make nearby plants prioritize microbial defenses over herbivory defenses, even when facing herbivorous attack.
Argument Flow: The passage establishes that plants have two distinct defense pathways and can communicate via airborne chemicals, then describes an experiment testing whitefly effects, and concludes that whiteflies disrupt normal defensive signaling by causing plants to signal for the wrong type of defense.
Text-Visual Synthesis: The graph quantifies the researchers' conclusion by showing that plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants produced less jasmonic acid (herbivory defense) and more salicylic acid (microbial defense) compared to controls, while plants exposed to whitefly-free air showed the expected increase in jasmonic acid.
Step 2: Interpret the Question Precisely
What's being asked? Which data from the graph best supports the researchers' conclusion
What type of answer do we need? Specific description of the graph data that provides evidence for the conclusion
Any limiting keywords? "best describes data from the graph" - must focus on the visual evidence, not just the text
Step 3: Prethink the Answer
- The researchers concluded that whiteflies make plants send signals that cause nearby plants to preferentially defend against microbial infection (produce more salicylic acid) even when under herbivorous attack (when they should produce more jasmonic acid)
- So the right answer should reference the key pattern in the graph:
- Plants exposed to whitefly-infested air produced less jasmonic acid than controls (wrong response to herbivory)
- Plants exposed to whitefly-infested air produced more salicylic acid than controls (microbial defense instead)
- This contrasts with plants exposed to whitefly-free air, which showed the normal response (more jasmonic acid)
- So the right answer should describe how the whitefly-infested air exposure group had reduced jasmonic acid and increased salicylic acid compared to controls, while the whitefly-free air group had the expected increase in jasmonic acid
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced more jasmonic acid than did control plants, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they produced less jasmonic acid and more salicylic acid than did control plants.
✓ Correct
- Accurately describes both comparison groups from the graph
- "More jasmonic acid than did control plants" matches whitefly-free air group (~205 vs ~140)
- "Less jasmonic acid and more salicylic acid than did control plants" matches whitefly-infested air group (~100 vs ~140 jasmonic; ~175 vs ~120 salicylic)
- Directly supports the conclusion by showing the contrasting responses
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they produced less jasmonic acid than salicylic acid, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced about the same amount of jasmonic acid and salicylic acid.
✗ Incorrect
- Claims whitefly-free plants produced "about the same" jasmonic and salicylic acid
- Graph clearly shows whitefly-free group: ~205 jasmonic vs ~130 salicylic (jasmonic much higher)
- Misrepresents the actual data relationships
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced both jasmonic acid and salicylic acid, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they exclusively produced salicylic acid.
✗ Incorrect
- Claims whitefly-infested plants "exclusively produced salicylic acid"
- Graph shows whitefly-infested plants produced ~100 ng/g jasmonic acid, not zero
- "Exclusively" is factually wrong based on visual data
When plants exposed to air from whitefly-infested plants were infested, they produced less jasmonic acid than did control plants, whereas when plants exposed to air from whitefly-free plants were infested, they produced more jasmonic acid and salicylic acid than did control plants.
✗ Incorrect
- Correctly identifies reduced jasmonic acid in whitefly-infested group
- Incorrectly claims whitefly-free plants produced more salicylic acid than controls
- Graph shows whitefly-free group: ~130 salicylic vs ~120 control (minimal difference, not "more")